 Developer Portal
Developer PortalUsing the API
API ScopesAPI CredentialsAPI LimitsAuthentication and AuthorizationAPI RequestsAPI ResponsesCustom Data FieldsUploading and Downloading DocumentsAPI EndpointsReporting EndpointsREST Hooks
REST Hooks and Event NotificationsWorking with Custom Data Fields
Introduction
The Actionstep API provides the capability to add custom data fields to both Matters and Participants to augment the data stored in Actionstep. In this tutorial we show how to use custom data fields to add additional data fields to new or existing Matters.
Prerequisites
This tutorial should be read in conjunction with the Custom Data Field Overview which provides a high-level overview of custom data fields in Actionstep, and is recommended reading before starting on this tutorial.
Sample Application
Our sample application also demonstrates the use of Custom Data Fields, the source code of which can be found in our public Actionstep GitHub repository.
Understanding How Custom Data Fields Work in Actionstep
The implementation of Custom Data Fields within Actionstep is divided into two parts. The first part is about defining the required data fields. This involves setting their name, data type, display label, and other properties. The second part is the consumption of the data fields (data entry) in Matters for which the data fields are available.
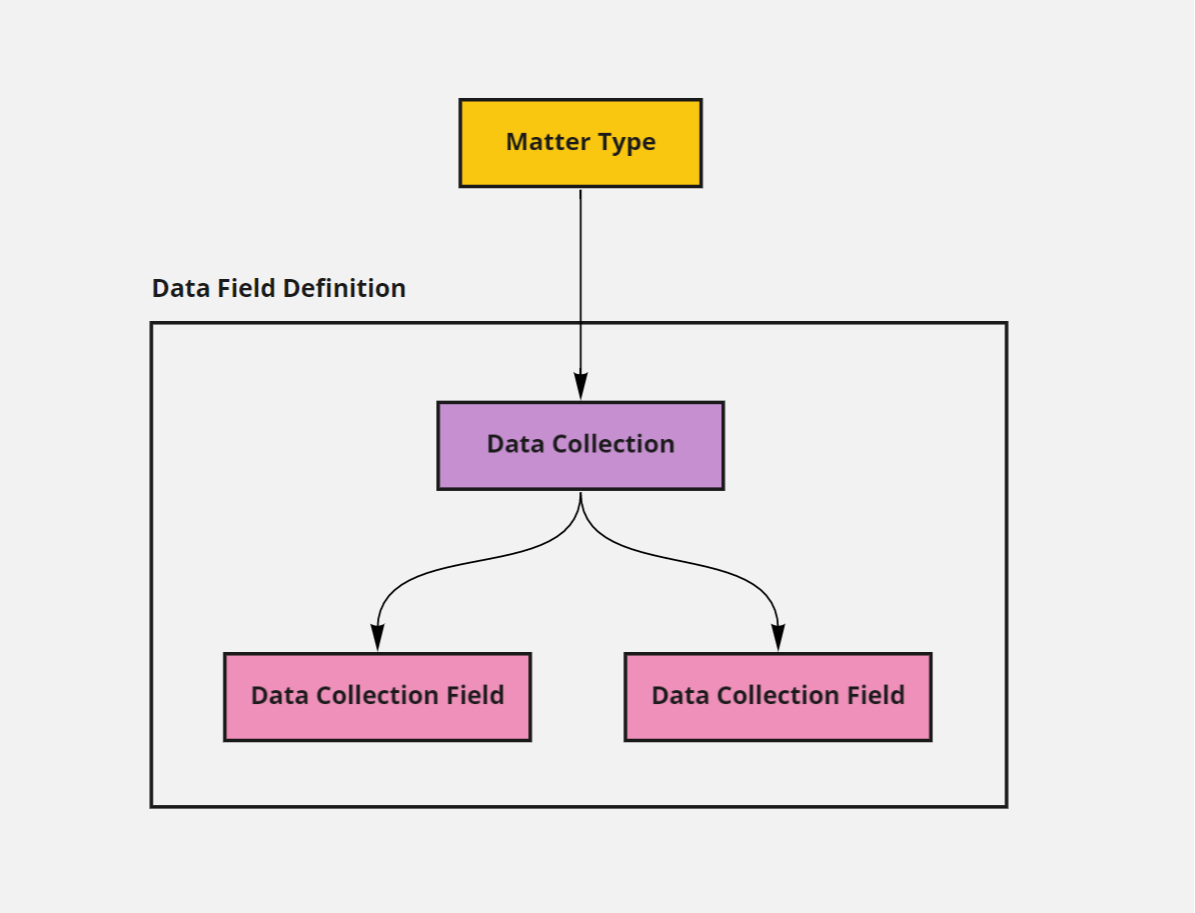
Data Field Definition
Custom data fields in Actionstep are associated with a Matter Type. When you create a new Data Collection you associate it to a specific Matter Type. The individual data fields you add to the Data Collection are therefore only available to Matters created from a particular Matter Type, i.e. they are not shared globally for all Matter Types. A Data Collection is a named group of individual Data Fields. When you create a new Data Field it is added to the specified Data Collection.
Data Field Consumption
Custom data fields are made available on the Matter page for users to enter data values into (or via the API). When data values are saved (for the first time) a new Data Collection Record is created. A Data Collection Record is used to link the data field values you enter to a specific Matter. When no custom data values are entered for a Matter no Data Collection Record is created, it is only created when data values are actually entered for a Matter for the first time. This logic will need to be incorporated into your API solution. A Data Collection Record will contain a set of Data Collection Record Value instances, one for each data field you are storing a value in.
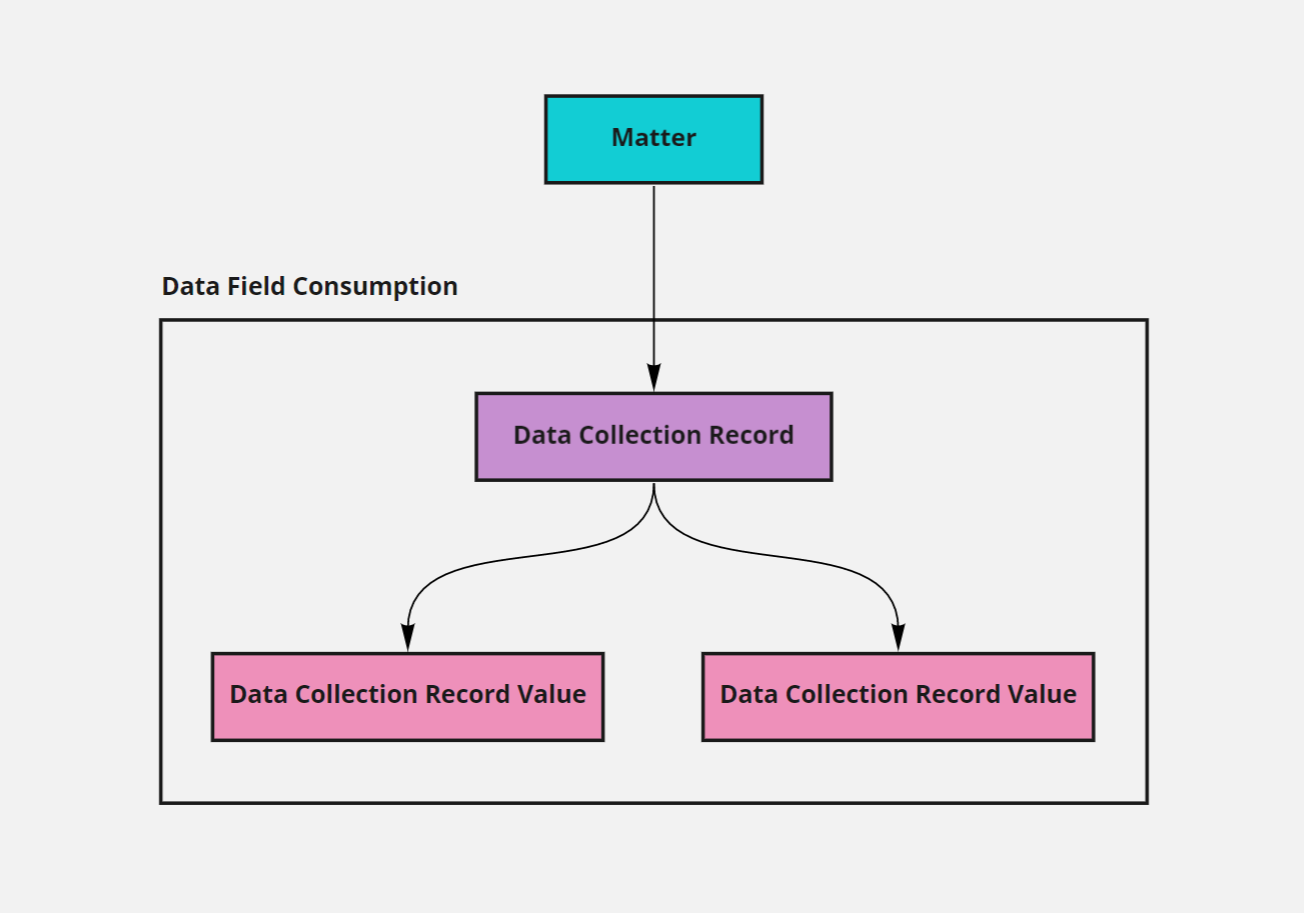
NB: If you clear the value from a stored data field, the Data Collection Record Value will remain and its value set to an empty string.
Creating a Data Collection
The first step is to create a Data Collection. A data collection is simply a named group of associated Data Fields. For example, a property conveyancing Matter might require additional fields to capture, for example, the number of bedrooms, the colour of the roof, and the material the house is constructed from. In this example, we may decide to hold these additional data values in a data collection called Property Attributes.
NB: By marking a Data Collection as multi-row you create a new record for a set of field instances. Using the example above this would mean if the Matter involved the purchase of multiple properties you could create a new record for each property, each record containing values for the the number of bedrooms, the colour of the roof, and the material the house is constructed from.
The first API request creates a new Data Collection. Since we already have an existing Conveyancing Purchase matter type (with an id of 11) we will associate our new Data Collection with this matter type. Note in this example we are not creating a multi-row Data Collection.
POST {api_endpoint}/api/rest/datacollections
{
"datacollections": {
"name": "property-attributes",
"description": "Buyers requested property details.",
"multipleRecords": "F",
"label": "Property attributes",
"links": {
"actionType": "11"
}
}
}
The response will be the following:
{
"links": {
"datacollections.actionType": {
"href": "https://ap-southeast-2.actionstepstaging.com.actionstep.com/api/rest/actiontypes/{datacollections.actionType}",
"type": "actiontypes"
}
},
"datacollections": {
"id": 30,
"name": "property-attributes",
"description": "Buyers requested property details.",
"multipleRecords": "F",
"order": null,
"label": "Property attributes",
"alwaysShowDescriptions": null,
"links": {
"actionType": "11"
}
},
...
}
Creating a Data Field
The next step is to create a new Data Field within our newly created Data Collection. For this tutorial we will create a new Data Field with the name of "number-of-bedrooms" which will be of data type Number. Notice we are associating this Data Field with the Data Collection created above by specifing its unique id in the links section. Repeat this API request for each Data Field you want to create within the Data Collection.
POST {api_endpoint}/api/rest/datacollectionfields
{
"datacollectionfields": {
"name": "number-of-bedrooms",
"dataType": "Number",
"label": "Number of bedrooms",
"links": {
"dataCollection": "30"
}
}
}
The response will be the following:
{
"links": {
"datacollectionfields.dataCollection": {
"href": "https://ap-southeast-2.actionstepstaging.com.actionstep.com/api/rest/datacollections/{datacollectionfields.dataCollection}",
"type": "datacollections"
},
"datacollectionfields.tag": {
"href": "https://ap-southeast-2.actionstepstaging.com.actionstep.com/api/rest/tags/{datacollectionfields.tag}",
"type": "tags"
}
},
"datacollectionfields": {
"id": "30--number-of-bedrooms",
"name": "number-of-bedrooms",
"dataType": "Number",
"label": "Number of bedrooms",
"formOrder": null,
"listOrder": null,
"required": "F",
"description": null,
"customHtmlBelow": null,
"customHtmlAbove": null,
"links": {
"dataCollection": "30",
"tag": null
}
},
}
Storing a Value in a Data Field
The sections above describe how to create the Data Field Definition. The following sections describe how to store an actual value in the Data Field for a given Matter.
When building an application you will need to implement appropriate logic to determine if there is an existing value stored for a Data Collection for a given Matter. This is best achieved by making a call to the datacollectionrecords endpoint specifying the Data Collection id and the Matter id. For example:
GET {api_endpoint}/api/rest/datacollectionrecords?dataCollection=30&action=7
NB: A Matter is often referred to as an action within the Actionstep API.
If no entry exists you will receive a '204 No Content' http status code.
Storing a field value for the first time requires two steps:
- Creation of a new Data Collection Record.
- Creation of a new Data Collection Record Value.
Creating a Data Collection Record
To create a new Data Collection Record make a POST request to the datacollectionrecords endpoint as shown below:
POST {api_endpoint}/api/rest/datacollectionrecords
{
"datacollectionrecords": {
"links": {
"action": "7",
"dataCollection": "30"
}
}
}
The response will be the following:
{
"links": {
"datacollectionrecords.action": {
"href": "https://ap-southeast-2.actionstepstaging.com.actionstep.com/api/rest/actions/{datacollectionrecords.action}",
"type": "actions"
},
"datacollectionrecords.dataCollection": {
"href": "https://ap-southeast-2.actionstepstaging.com.actionstep.com/api/rest/datacollections/{datacollectionrecords.dataCollection}",
"type": "datacollections"
}
},
"datacollectionrecords": {
"id": 23,
"canWrite": "F",
"canDelete": "F",
"links": {
"action": "7",
"dataCollection": "30"
}
},
...
}
Creating a Data Collection Record Value
This step actually stores the Data Field value in the Actionstep database. This is achieved by making a PUT request to the datacollectionrecordvalues endpoint specifying the value to be stored. The called url includes a composite identifier (in this example: "30--number-of-bedrooms--23") which is composed of three component parts:
- "30" is the Data Collection id.
- "number-of-bedrooms" is the name of the field.
- "23" is the Data Collection Record id.
Note all Data Field values are stored as strings and converted to their underlying data type when performing validation checks and for display formatting (where appropriate).
PUT {api_endpoint}/api/rest/datacollectionrecordvalues/30--number-of-bedrooms--23
{
"datacollectionrecordvalues": {
"stringValue": "4"
}
}
The response will be the following:
{
"links": {
"datacollectionrecordvalues.action": {
"href": "https://ap-southeast-2.actionstepstaging.com.actionstep.com/api/rest/actions/{datacollectionrecordvalues.action}",
"type": "actions"
},
"datacollectionrecordvalues.dataCollectionField": {
"href": "https://ap-southeast-2.actionstepstaging.com.actionstep.com/api/rest/datacollectionfields/{datacollectionrecordvalues.dataCollectionField}",
"type": "datacollectionfields"
},
"datacollectionrecordvalues.dataCollectionRecord": {
"href": "https://ap-southeast-2.actionstepstaging.com.actionstep.com/api/rest/datacollectionrecords/{datacollectionrecordvalues.dataCollectionRecord}",
"type": "datacollectionrecords"
},
"datacollectionrecordvalues.dataCollection": {
"href": "https://ap-southeast-2.actionstepstaging.com.actionstep.com/api/rest/datacollections/{datacollectionrecordvalues.dataCollection}",
"type": "datacollections"
}
},
"datacollectionrecordvalues": {
"id": "30--number-of-bedrooms--23",
"stringValue": "4",
"links": {
"action": "7",
"dataCollectionField": "30--number-of-bedrooms",
"dataCollectionRecord": "23",
"dataCollection": "30"
}
},
...
}
Notice the links section from the response contains the keys and identifiers to the other components in the data fields ecosystem. You can use these values to perform seaches when building an application with complex functionality.
To verify the value has been stored make a GET request to the datacollectionrecordvalues endpoint specifying the unique composite identifier as described above:
GET {api_endpoint}/api/rest/datacollectionrecordvalues/30--number-of-bedrooms--23
Updating Multiple Data Field Values in a Single Request
You can update more than one data field value in a single PUT request so long as the request body includes the descriptors for each field, for example:
PUT {api_endpoint}/api/rest/datacollectionrecordvalues/231--Date--1726,231--Description--1726
{
"datacollectionrecordvalues": [
{
"id": "231--Date--1726",
"stringValue": "2022-11-10",
"links": {
"action": "1644",
"dataCollectionField": "231--Date",
"dataCollectionRecord": "1726",
"dataCollection": "231"
}
},
{
"id": "231--Description--1726",
"stringValue": "something descriptive",
"links": {
"action": "1644",
"dataCollectionField": "231--Description",
"dataCollectionRecord": "1726",
"dataCollection": "231"
}
}
]
}
Data Field Data Types
There are a number of different data types you can select from when creating a Data Field. Below is a list of the most commonly used data types together with the parameter value to specify for the dataType property in the message body when posting to the datacollectionfields endpoint.
| Data Type | Parameter Value |
|---|---|
| String | String |
| Number | Number |
| Money | Money |
| Date | DateNM |
| Boolean | Boolean |
Summary
In this tutorial we showed how to create a custom Data Field Definition associated with a given Matter Type. We then showed how to store a value for this Data Field in the Actionstep database and subsequently retrieve its value.